A research team at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has developed a new alloy that maintains its strength and ductility across extreme temperatures ranging from –196 °C to 600 °C. The findings, which have drawn attention from the aerospace and automotive industries, were published in the journal Materials Research Letters. The team was led by Professor Hyoung Seop Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Graduate Institute of Ferrous Technology, and Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Most metals used in everyday life are sensitive to temperature changes—metal doorknobs feel icy in winter and hot in summer. Consequently, conventional metal materials are typically optimized for performance within a narrow temperature range, limiting their effectiveness in environments with dramatic temperature fluctuations.
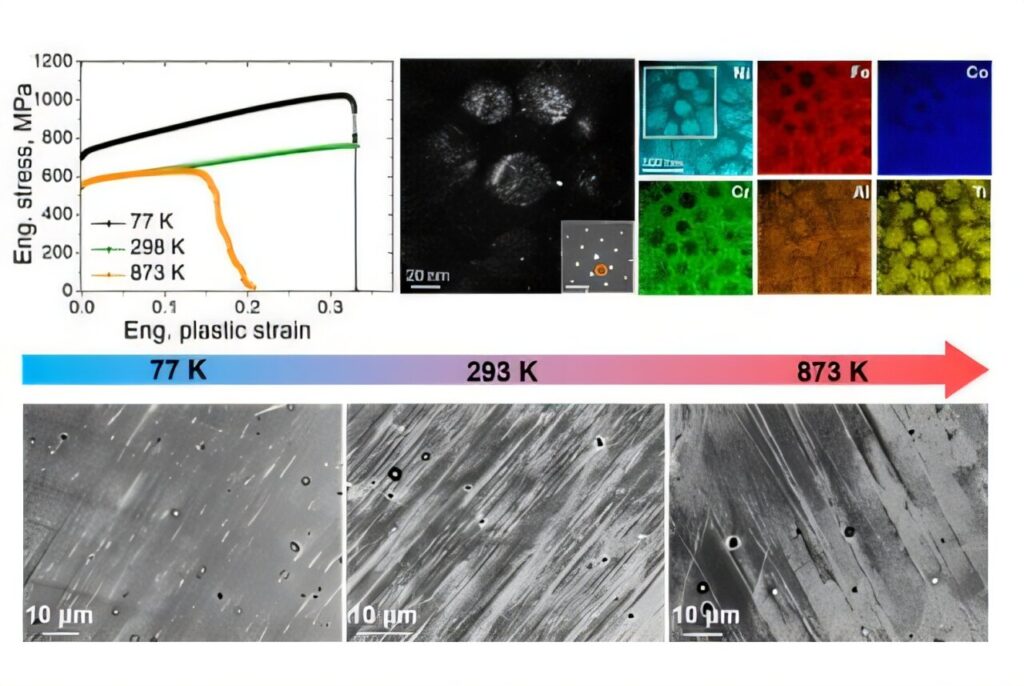
To overcome this challenge, the POSTECH research team introduced the concept of the “Hyperadaptor” and developed a nickel-based high-entropy alloy (HEA) that embodies this idea.
The newly developed HEA
The newly developed HEA demonstrates nearly constant mechanical performance across a wide temperature range—from cryogenic conditions at -196°C (77 K) to high heat at 600°C (873 K). This remarkable stability is attributed to the presence of nanoscale L1₂ precipitates, which are uniformly distributed within the alloy. These fine particles act as reinforcements that inhibit deformation, while the alloy’s internal structure accommodates stress through consistent slip behavior, regardless of temperature.
This development holds significant promise for applications that involve sudden or extreme temperature changes, such as rocket or jet engines, automotive exhaust systems, power plant turbines, and pipelines. The alloy’s ability to maintain stable performance under such conditions can greatly enhance both safety and efficiency in these demanding environments.
“Our HEA breaks through the limitations of existing alloys and establishes a new class of temperature-insensitive materials,” said Professor Kim. “The Hyperadaptor concept represents a breakthrough in developing next-generation materials with consistent mechanical behavior even under extreme conditions.”
More information:
Hyojin Park et al, Hyperadaptor; Temperature-insensitive tensile properties of Ni-based high-entropy alloy a wide temperature range, Materials Research Letters (2025). DOI: 10.1080/21663831.2025.2457346
Citation:
‘Hyperadaptor’ alloy with stable properties stands strong across extreme temperatures (2025, April 16)
retrieved 17 April 2025
from https://techxplore.com/news/2025-04-hyperadaptor-alloy-stable-properties-strong.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.